
By 2026, human resources has completely changed. It is no longer just about paperwork or policies. HR now plays a key role in shaping business strategy and helping organizations grow. This shift is powered by advanced technology, especially AI and modern Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS). These systems go beyond storing records. They help manage hiring, employee growth, performance, and workforce planning in one place. In a fast-moving, digital world, HRMS gives companies the tools to adapt, support their people, and stay competitive.
What Exactly is an HR Management System (HRMS)?
A Human Resource Management System (HRMS) is an integrated software suite meticulously designed to automate and centralize an organization’s HR functions. Unlike rudimentary Human Resources Information Systems (HRIS) that primarily focused on data storage, today’s HRMS platforms seamlessly merge administrative tasks with strategic talent management initiatives.
Modern HRMS solutions, predominantly cloud-based, empower HR professionals to manage diverse aspects of the workforce efficiently. They combine routine operational necessities like payroll and benefits administration with more complex strategic elements such as performance management, learning, and predictive analytics. This integration fosters a single source of truth for all people-related data, crucial for data-driven decision-making and ensuring adherence to complex regulatory landscapes across different geographies.
Core Modules of Integrated HRMS
A comprehensive HRMS is architected around a series of interconnected modules, each meticulously designed to address specific facets of human resource management. The true power of an HRMS lies in the seamless flow of information between these modules, eradicating data silos and enhancing operational synergy.

The Central Data Repository: Employee Database
The employee database, often referred to as Core HR, forms the fundamental backbone of any HRMS. It centrally stores critical employee information, including personal details, job roles, organizational hierarchies, and employment histories. This singular repository ensures data accuracy, reduces redundancy, and lays the groundwork for robust reporting and compliance. It is where all employee lifecycle events are meticulously tracked, providing an invaluable historical record and real-time overview.
Cultivating Talent: Recruitment and Onboarding
Modern HRMS platforms incorporate sophisticated recruitment and onboarding functionalities. Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) streamline the entire hiring process, from job posting across various platforms to candidate tracking, interview scheduling, and offer management. Once an offer is accepted, the onboarding module takes over, automating paperwork, IT provisioning, and orientation tasks, ensuring a smooth and engaging transition for new hires. This focus on an exceptional candidate and new employee experience contributes significantly to retention rates.
Ensuring Accuracy: Payroll and Benefits Administration
Payroll and compensation modules are pivotal for ensuring accurate and compliant remuneration. These systems automate salary calculations, tax withholdings, and pay disbursements, drastically reducing the margin for error often associated with manual processes. Furthermore, benefits administration enables employees to enroll in and manage healthcare, retirement plans, and other benefits, with the system automatically tracking eligibility and ensuring regulatory adherence, which is vital for maintaining compliance with tax and labor laws.
Strategic Insight: Analytics and Reporting
At the highest level, HRMS platforms deliver powerful analytics and reporting capabilities. Dashboards and custom reports aggregate vast amounts of HR data, providing real-time insights into key metrics such as turnover rates, hiring efficiency, compensation trends, and workforce diversity. This intelligence is invaluable for strategic workforce planning, predictive modeling, and validating the return on investment of HR initiatives, transforming HR into a truly data-driven function.
Transformative Benefits: Driving Organizational Excellence
The adoption of a sophisticated HRMS offers a cascade of benefits that extend far beyond the HR department, impacting overall organizational health and strategic agility. These advantages are particularly pronounced in the complex operational environment of 2026.
Unleashing Efficiency and Automation
An HRMS makes daily HR work much easier by automating tasks like payroll, leave requests, and benefits. This saves time and reduces errors. Instead of handling paperwork, HR teams can focus on people, growth, and building a better workplace.
Enabling Data-Driven Decision Making
An HRMS brings all employee data into one place and gives leaders real-time insights. With simple dashboards, they can track hiring progress, retention, and training results. This helps businesses plan future staffing, spot skill gaps, and make smarter decisions based on facts, not guesswork.
Elevating Employee Engagement and Experience
An HRMS also improves the employee experience. With self-service tools and clear feedback systems, employees feel more valued and connected. Easy access to information makes HR support simple and smooth. When people feel heard and supported, their morale, productivity, and loyalty naturally grow.
Realizing Cost Savings and Scalability
Using one HRMS instead of many separate tools helps companies save money and reduce extra work. Cloud-based systems offer flexible pricing, making costs easier to manage. As businesses grow or hire more people, the system can scale easily. Over time, fewer errors and less manual work improve overall savings.
The AI Revolution in HR
AI is no longer a developing technology, it has matured into a baseline competency and a core driver of HR strategy. Organizations are forming AI Leadership Coalitions where HR plays a critical role in shaping AI adoption and ensuring cultural alignment. HR’s involvement in identifying tasks suitable for automation is crucial, with advanced companies being 2.5 times more likely to involve HR in this process. AI is projected to free up over 120 hours per employee per year, and HR’s strategic mandate is to reinvest this reclaimed capacity into higher-value activities like innovation and reskilling.
However, this rapid integration also presents challenges. Only 35% of HR professionals currently feel equipped to use AI effectively. This underscores the urgency for AI fluency the ability to use, question, and responsibly apply AI to become a critical differentiator for HR practitioners. An HRMS, particularly one with integrated generative AI capabilities for tasks like drafting job descriptions or sentiment analysis, becomes the conduit for this fluency.
Navigating the HR Tech Landscape: Choosing the Right HRMS
With the HR technology market projected to triple by 2030, selecting the optimal HRMS is a critical strategic decision. The right choice can profoundly influence an organization’s efficiency, compliance, and competitive edge. Key selection criteria for 2026 demand a forward-thinking approach:
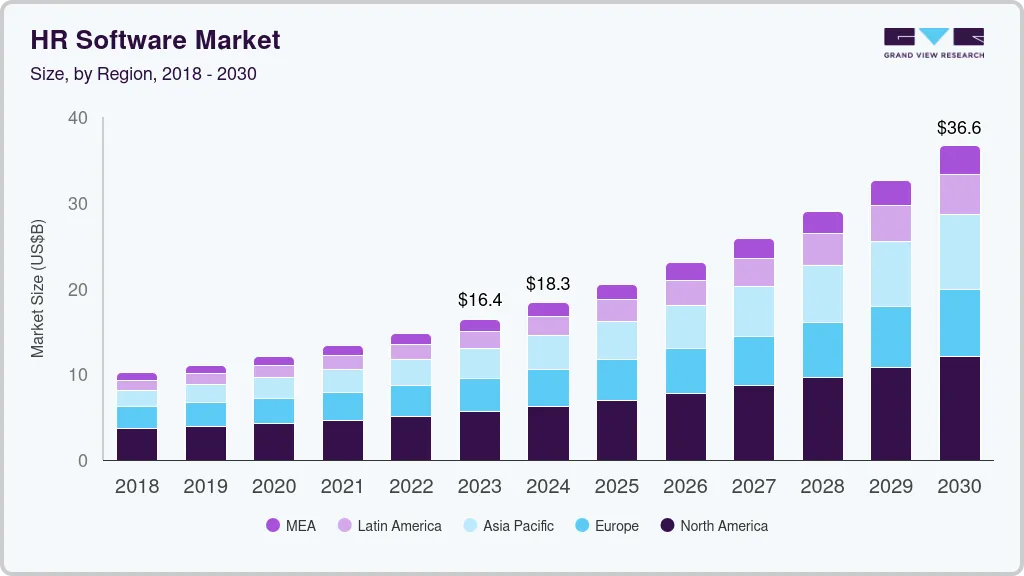
Source: grandviewresearch.com
AI Integration: Does the platform offer embedded AI capabilities for automation, predictive analytics, or generative tasks?
Integration Capabilities: Can it seamlessly connect via Open APIs with existing ERP, accounting, and communication tools (e.g., Slack, MS Teams) to create a cohesive digital ecosystem?
User Experience (UX): Is the interface intuitive and user-friendly for both employees and managers, ensuring high adoption rates and minimizing training overhead?
Compliance Coverage: Does it automatically update to reflect evolving local and international labor laws, such as India’s 2025 Labour Codes or UAE Labour Law?
Scalability: Is the system cloud-based and flexible enough to grow with the organization, supporting expansion from small teams to enterprise-level workforces without significant disruption?
Security Standards: Does the vendor adhere to robust security certifications like ISO 27001,
SOC 2, or GDPR, safeguarding sensitive employee data?
Effective implementation also demands strategic alignment. Organizations should identify critical pain points to automate first, engage key stakeholders in pilot testing, and ensure the chosen system aligns with long-term business objectives, such as improving retention or identifying high-potential talent for succession planning. A thorough evaluation, considering both current needs and future strategic imperatives, is paramount for a successful HRMS deployment.
Conclusion
As organizations navigate the complexities of 2026, a modern HRMS stands at the center of strategic transformation. By integrating automation, analytics, employee experience tools, and AI-driven capabilities, it empowers HR to move beyond administration into true business leadership. From improving efficiency and compliance to enabling data-driven decisions and scalable growth, the value of an integrated HRMS is undeniable. Companies that thoughtfully select and implement the right platform will strengthen workforce agility, enhance performance, and build a sustainable competitive advantage in an increasingly digital world.





