The integration of artificial intelligence into the modern workforce represents a fundamental and irreversible transformation of labor, surpassing the scope and speed of previous technological shifts. We are moving beyond AI as a mere tool for automation and into an era of profound human-AI augmentation. This evolution is giving rise to a new organizational model, where humans and autonomous AI agents operate in symbiotic, hybrid teams to drive unprecedented gains in workplace productivity, innovation, and value.
The Breakneck Surge: A New Economic Reality
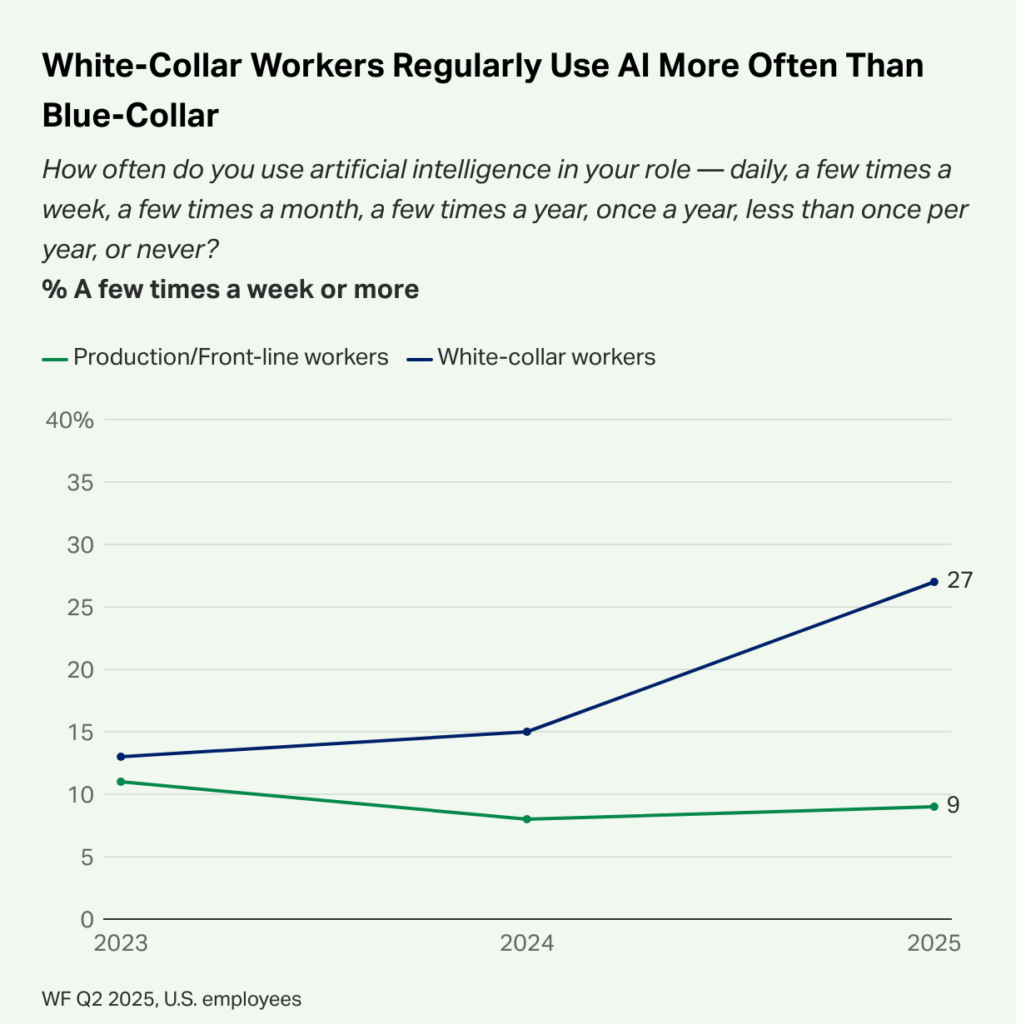
The speed of AI adoption has no historical precedent. In the United States, a staggering 40% of employees now report using AI at work, a figure that has doubled from just 20% in 2023. This is not a trend confined to Silicon Valley over three-quarters of organizations globally now leverage AI in at least one business function. The global AI market is on a trajectory to surpass $240 billion in 2025, fueled by sustained annual growth rates of 20-35%.
[Source:www.gallup.com]
However, a critical maturity gap exists despite 92% of organizations planning to increase AI investments, indicating that most are still in experimental phases rather than achieving full, scaled workflow integration. This highlights a crucial distinction through isolated pilots, but through the fundamental redesign of how work gets done.
Prioritizing Capabilities Over Cost
A common misconception is that businesses adopt AI primarily to cut costs. The data reveals a more strategic rationale. Analysis of API usage shows weak price sensitivity, suggesting that the decision to deploy AI is driven not by its price tag but by the unique capabilities and economic value it can unlock. This value-driven approach is already yielding tangible results. The study found that 51% of small-to-medium-sized businesses that adopted generative AI reported a revenue increase of 10% or more.
The Agent-Centric Organization
The most profound impact of AI is the transformation of work from simple automation to a new era of human-AI augmentation. AI is increasingly viewed as a collaborative partner, freeing human workers to focus on more strategic, creative, and people-centric tasks.
Culminating this evolution is the emergence of the AI agent, a new class of digital collaborator. Unlike reactive assistants or rule-based bots, AI agents are software systems designed to autonomously pursue goals and complete complex, multi-step tasks. They possess a high degree of autonomy, the ability to learn and adapt, and demonstrate reasoning, planning, and memory.
This distinction is critical. An agent can independently manage a project, coordinate parallel tasks, and reroute operations to build resilience, fundamentally changing how organizations scale. The strategic question shifts from “How many people do we need?” to “What system of agents can we build to achieve this goal?”
| Aspect | Bot | AI Assistant | AI Agent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Automates simple, pre-defined tasks or conversations. | Assists users with tasks upon request. | Autonomously and proactively performs complex tasks to achieve a goal. |
| Autonomy | Least autonomous; follows pre-programmed rules. | Less autonomous; requires user input and direction. | Highest degree; operates independently and makes decisions. |
| Capabilities | Basic interactions, limited learning. | Responds to requests, completes simple tasks, recommends actions. | Complex, multi-step actions; learns and adapts; demonstrates reasoning and planning. |
| Interaction | Reactive; responds to triggers or commands. | Reactive; responds to user requests. | Proactive; goal-oriented and self-directed. |
Quantifiable Gains
The impact of AI is no longer theoretical but produces documented, quantifiable business outcomes across every major industry. The new return on investment is measured not just in system efficiency but in human time saved and creative output unlocked. For a focused analysis on how AI for operational efficiency at the organizational level, see our article on AI’s Role in Enhancing Workplace Efficiency.
The gains are specific and transformative:
- Error Reduction: Automated processes in billing, compliance, and data entry have lowered error rates by up to 85%.
- Shift to Creation: In software development, AI has caused a net 7.4 percentage point shift from debugging existing code to creating new code, demonstrating its power to enable higher-order work.
- Employee Satisfaction: When positioned as a collaborator, AI boosts morale. Over 80% of AI professionals report positive job satisfaction, citing improved work-life balance and career opportunities.
Challenges and Ethical Imperatives
Industry | Company / Sector Example | AI Application | Quantifiable Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
Healthcare | Cleveland Clinic | Patient flow and scheduling optimization | Reduced patient wait times by 30% and improved scheduling by 45%. |
Healthcare | Diagnostic Imaging | AI-assisted cancer detection | Reduced error rates in cancer detection by nearly 10%. |
Finance | JPMorgan | Legal document intelligence | Reduced manual review from 360,000 hours per year to seconds with major accuracy gains. |
Manufacturing | Toyota | Factory operations optimization | Reduced over 10,000 workforce hours per year |
Manufacturing | General Electric | Predictive maintenance | Reduced maintenance costs by up to 25% and downtime by 30%. |
Retail | Amazon / Netflix | Personalized recommendation engines | Generates up to 35–80% of sales and content discovery. |
While AI offers substantial benefits, its implementation requires a strategic approach that confronts critical challenges head-on. Successful integration is not just a technical feat but an ethical and organizational one.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
AI systems can inherit and amplify human prejudices present in their training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes in hiring, lending, or healthcare. Addressing this requires a multidisciplinary approach, including regular audits, diverse development teams, and the involvement of ethicists and social scientists. The goal is not just to build powerful AI, but to design human-centered frameworks that avoid replicating our own flaws.
Data Security
AI systems require vast amounts of sensitive data, making them prime targets for sophisticated cyberattacks. It is no surprise that 40-50% of companies list data privacy and security as their leading concern. This creates a crisis of trust and accountability, especially in high-stakes fields. The industry’s push toward explainable AI is not just a technical goal but a prerequisite for building trust.
Workforce Transition and Job Displacement
The transition to an AI-powered workforce will inevitably cause disruption. Widespread adoption could displace 6-7% of the US workforce, leading to a period of frictional unemployment as workers transition to new roles. AI has already been eliminated and is taking over entry-level white-collar roles in marketing, design, and customer service at a higher risk.
However, this is not a story of pure replacement. By 2030, an estimated 70% of skills used in most jobs will change, creating demand for entirely new roles like AI Ethics Specialist, Prompt Engineer, and AI Workforce Manager. Professions requiring uniquely human qualities of empathy, complex judgment, and creativity are less likely to be replaced and will instead be augmented. The imperative for organizations and policymakers is to create a new social contract, managing this transition through proactive reskilling programs and supportive policies.
A Strategic Roadmap for the AI-Powered Future
The bottleneck to AI success lies not with workforce resistance but at the leadership and governance level. A strategic, human-centric approach is essential for harnessing AI‘s full potential while mitigating its risks.
Key Recommendations for Executive Leadership
Lead from the Front: C-suite leadership is crucial. Champion AI adoption, clearly align its use with organizational goals, and build confidence across teams.
- Reimagine Workflows from the Ground Up: The greatest value comes not from plugging AI into existing processes but from reinventing how work gets done. Center this redesign on new human-AI partnerships with agents at the core.
- Invest in AI Literacy as a Core Competency: Make AI fluency a foundational skill for all employees. Empower internal mentors to foster a culture of continuous, intergenerational learning.
- Establish Proactive Governance: Implement a comprehensive strategy to manage ethical challenges. Create multidisciplinary oversight teams, conduct regular audits for bias, and adopt robust cybersecurity measures.
- Develop a Talent Transition Strategy: Acknowledge the reality of frictional unemployment. Proactively identify roles at risk and offer targeted reskilling and retraining programs to ensure a just and equitable transition.
- Measure Human-Centric Outcomes: Move beyond traditional ROI. Assess AI’s impact on human performance by measuring judgment quality, employee satisfaction, and creative output to capture its true value as an amplifier of human capability.
Conclusion
AI for future workforce is already arriving. It is a future defined not by a contest between humans and machines, but by their collaboration. The organizations that will thrive are those that build this future with intention, placing human judgment, creativity, and well-being at the very center of their AI-powered strategy. The revolution is here, and it calls for a new generation of leadership to guide it.





